Contents
Homework Due THIS CLASS
- All parts of Project #3 are DUE!
- Post your work to the class site following the Deliver > Documentation & Feedback guidelines.
- If you didn’t contribute to the Visual Library yet this week, do so!
Materials Needed THIS CLASS
- flash/thumb drive
Visual Library
Let’s designate a facilitator to take a look at your new Visual Library posts. Try to use the vocabulary from Project #3.
Review: Project #3 Concepts
- Value: Signifies the relative differences of light and dark
- Achromatic Value: Value with the absence of hue (color).
- Grayscale: The full range of values simplified into a graduated scale.
- Narrow Value Range: When the values congregate around the dark (low-key), middle (middle-key), or light (high-key) part of the grayscale.
- Broad Value Range: When the values are spread over the dark, middle, and light part of the grayscale.
- Shadow: Dark area of an object as a result of a disruption of the light source.
- Highlight: Portion of an object that receives the greatest amount of direct light
- Contrast: Occurs when elements are unrelated or dissimilar in value, size, shape, etc.
- Chiaroscuro/Tenebrism: Forceful use of contrasting lights and darks, creating a dramatic mood.
- Film Noir: a cinematic term used to describe a visual style that emphasizes low-key lighting and unbalanced compositions.
- Focal Point: The elements or objects on which the viewer’s attention is focused.
- Rule of Thirds: A compositional guideline, where an image is divided into nine equal parts using two horizontal and two vertical lines. Important elements should be placed along these lines or their intersections to create tension, energy and interest.

Carrie Mae Weems 
Joel Meyerowitz 
CF Napa- Edge Wine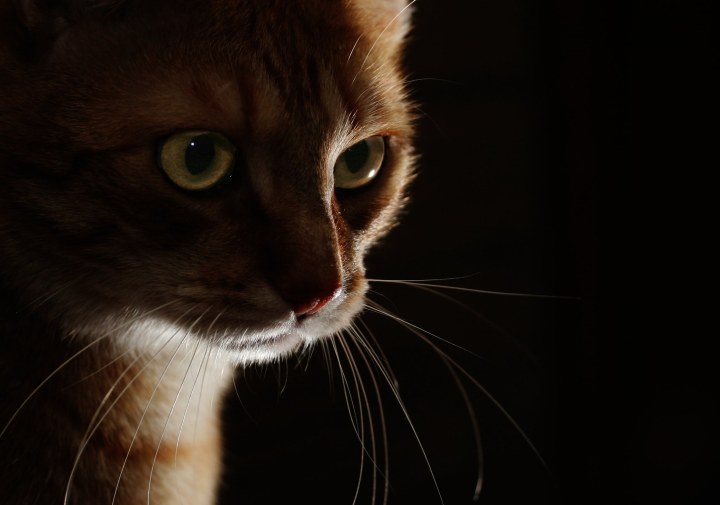 
Dramaticat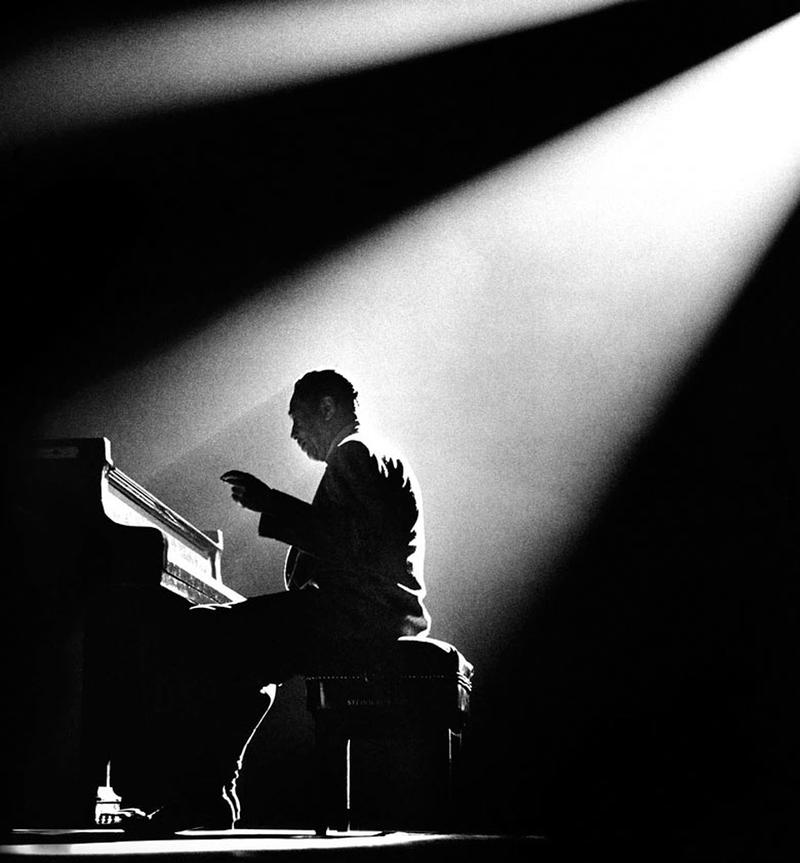 
Herman Leonard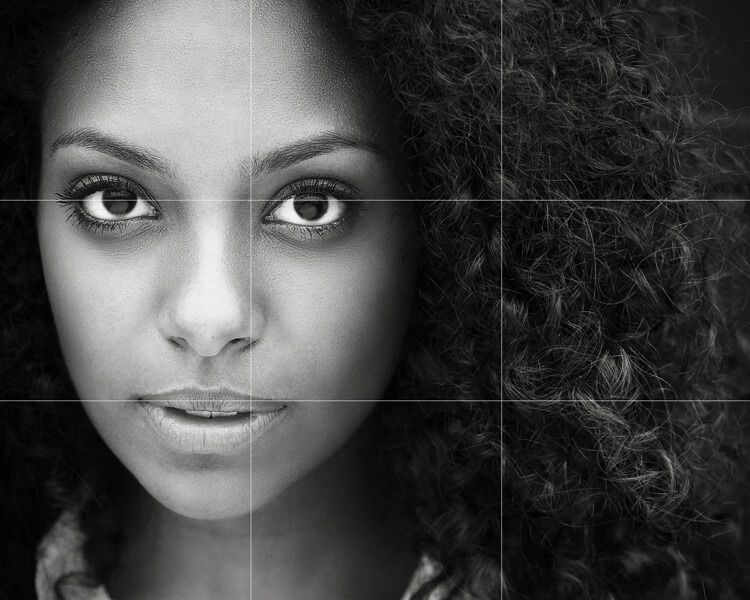 
blog.katchup.com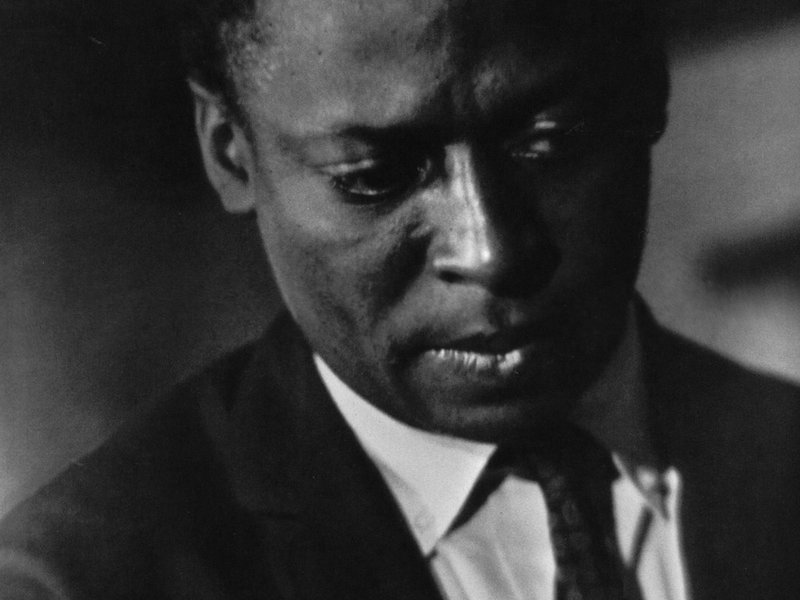 
Roy DeCarava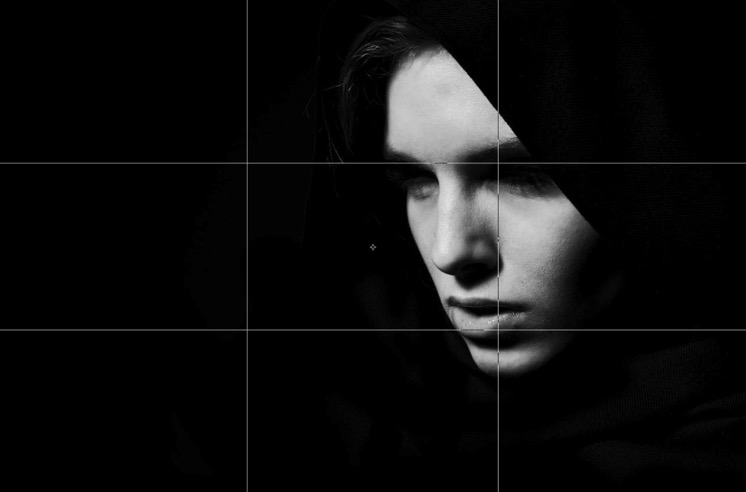 
videoschoolonline.com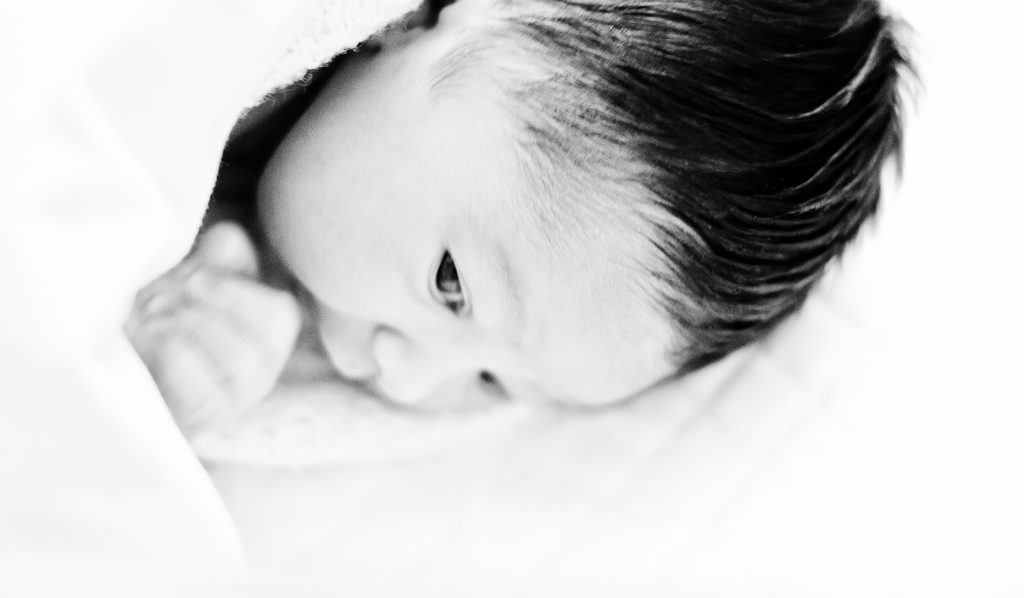 
Critique
Bring your finished animated gif up to the front computer to present.
Let’s use the project vocabulary to speak about the final work. We will go around the class and each student will contribute their impressions of the work presented using three concepts from the Project #3 vocabulary.
Discussion: Color
Questions
- What is color? And how do we see it?
- What are Primary and Secondary Colors?
- What is a color wheel?
What is Color?
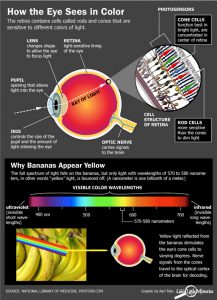
When light hits objects, some of the wavelengths are absorbed and some are reflected, depending on the materials in the object. The reflected wavelengths are what we perceive as the object’s color.
Visible light is made of seven wavelength groups. These are the colors you see in a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.

How do we see color?
Our eyes are the input channels for this light and our retina contains different types of light sensors.
- Rods: record brightness and darkness (value).
- Cones: Each one optimized to absorb a different spectrum range of visible light.
- One set absorbs long, low-frequency wavelengths, the reds.
- Another absorbs mid-size wavelengths, the greens.
- The third absorbs short, high-frequency wavelengths, the blues.
Watch these short videos to understand how and why we see color:
- What is color? – Colm Kelleher
- How we see color – Colm Kelleher
- Finding the Origins of Human Color Vision – PBS.org
Color Wheel
A color wheel is an organization of hues around a circle. It is a tool used to help us understand color relationships and is traditional in the field of art and design. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors in 1666. Since then, scientists and artists have studied and designed numerous variations of this concept.
We are going to look at two kinds of color wheels. Traditional (used for fine art/painting) and Digital (CYMK & RGB).
Traditional Color Wheel
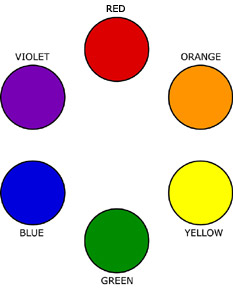
- Primary Colors: Red, Yellow, Blue
- Secondary Colors: Orange, Green, Violet
- Red + Yellow = Orange
- Yellow + Blue = Green
- Blue + Red = Violet
Digital Color Wheel
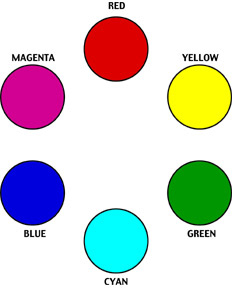
CYMK Color Model:
- Primary Colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow
- Secondary Colors: Red, Green, Blue
- Yellow + Cyan = Green
- Yellow + Magenta = Red
- Cyan + Magenta = Blue
RGB Color Model:
- Primary Colors: Red, Green, Blue
- Secondary Colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow
- Blue + Green = Cyan.
- Blue + Red = Magenta
- Red + Green = Yellow
New Vocabulary
- Hue: Designates the common name of a color, determined by the specific wavelength of a ray of light and/or its position in the spectrum or color wheel.
- Primary Colors/Triad: Three colors when mixed in equal or unequal amounts can produce a variety of colors.
- Traditional primary colors are: Red, Yellow, Blue
- Digital Primary Colors: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow
- Secondary Colors/Triad: Colors created by mixing equal proportions of any two primary colors.
- Traditional secondary colors are: Orange, Green, Violet
- Digital Secondary Colors: Red, Green, Blue
- Complementary Colors: colors opposite each other on the color wheel.
Lab: Starter Color Wheel
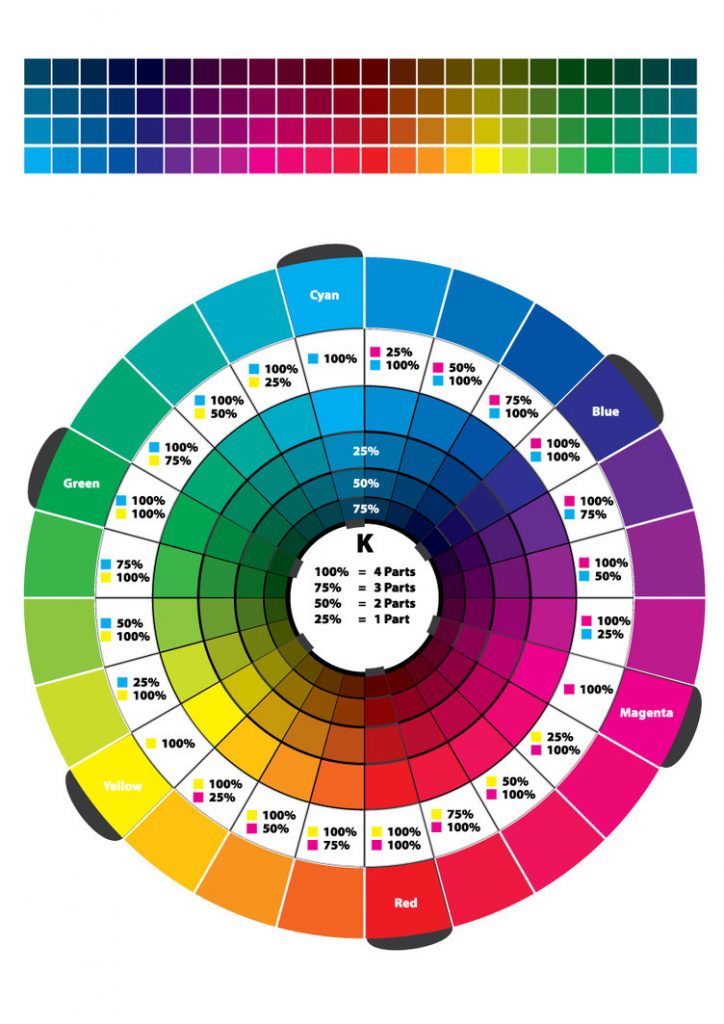
- Review this documentation about understanding color in Photoshop.
- Using the photoshop template file provided, work independently to accurately fill in the color wheel using the Paint Bucket and CMYK Color palette sliders.
- Start with the primary triad from the CYM system (Cyan, Yellow, Magenta)
- Then fill in the RYB system (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet) using the CYM percentages in the color wheel above.
- Save the file as firstnamelastname_ColorWheel.psd
Homework Due Next Class
- Take the combined Project #2 & #3 Quiz!
- Finish the Starter Color Wheel introduced in class and bring to next class to continue working.
- If you haven’t already, post your Project #3 work to the class site and comment on a fellow student’s work using the Deliver > Documentation & Feedback guidelines.
- If you didn’t contribute to the Visual Library yet this week, do so!
Materials Needed For Next Class
NOTE: Points are deduced from your final participation grade if you repeatedly come to class without your materials.
- flash/thumb drive (with completed ColorWheel.psd)
- color wheel (small)
- 4 small containers to hold paint
- (little plastic sauce containers work well!)
- set of large, medium, and small brushes
- (save 40% with Michaels coupon code 40BRUSH11319)
- palette (round 10-well) or takeout container
- cotton rags (old t-shirt) or roll of paper towels
- two water containers (yogurt cups, soda bottles with tops cut off, soup cans)