November 12, 2018
What’s Due?
Check to make sure you have completed ALL PARTS OF Project #3.
- Turn in mounted Broad-Range Collage, Narrow-Range Collage, Painting, and Digital Collage
Materials Needed
- Print out this Template
- mini color wheel
- Reeves Gouache 12 Paint Set or Savoir Faire Gouache 10 Paint Set or Utrecht Designer Gouache, Set of 8 – Primaries
- brushes
- ruler
- t-square
- pencils
- 9×12″ bristol.
Critique
- Hang up your finished, mounted Broad-Range Painting & Broad-Range Collage and Narrow-Range Digital Collage & Narrow-Range Collage
Lecture/Discussion
- What is color? And how do we see it?
- What are Primary and Secondary Colors?
- What do the CMY, RGB, and RYB color models represent?
- What is a color wheel?
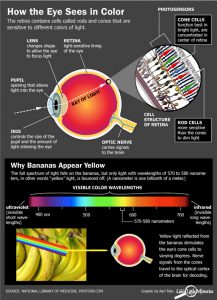
Introducing Color: When light hits objects, some of the wavelengths are absorbed and some are reflected, depending on the materials in the object. The reflected wavelengths are what we perceive as the object’s color.
Visible light is made of seven wavelength groups. These are the colors you see in a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Our eyes are the input channels for this light and our retina contains different types of light sensors.
- Rods: record brightness and darkness (value).
- Cones: Each one optimized to absorb a different spectrum range of visible light. (1) One set absorbs long, low-frequency wavelengths, the reds. (2) Another absorbs mid-size wavelengths, the greens. (3) The third absorbs short, high-frequency wavelengths, the blues.
Watch these short videos to understand how and why we see color:
- What is color? – Colm Kelleher
- How we see color – Colm Kelleher
- Why do we see color? Finding the Origins of Human Color Vision – PBS.org
NEW Vocabulary:
- Hue: Designates the common name of a color, determined by the specific wavelength of a ray of light and/or its position in the spectrum or color wheel.
- Primary Colors: Three colors when mixed in equal or unequal amounts can produce a variety of colors. Traditional primary colors are: Red, Yellow, Blue
- Secondary Colors: Colors created by mixing equal proportions of any two primary colors. Traditional secondary colors are: Orange, Green, Violet
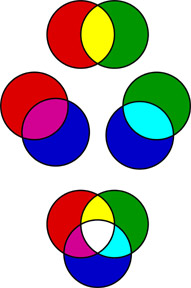
RGB Additive Color Model (Light/Digital)
Humans can perceive three primary colors of light: red, green and blue. When overlaid or “added together”, they produce the secondary colors of light: yellow, cyan and magenta as in the diagram. Your digital devices all rely on RGB light to produce all the colors your see on screen.
- Red and green light together are perceived as yellow.
- Blue and green light together are perceived as cyan.
- Blue and red light together are perceived as magenta.
- All the other perceived colors can be produced by blending specific amounts of red, green and blue light.
- White light can be produced by mixing a color light and its opposite or equal amounts of red, green and blue light.
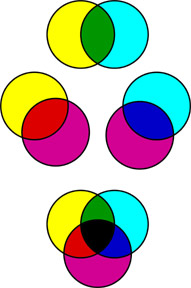
CMY Subtractive Color Model (Printing / Pigment / Real Life)
The absorption and reflection of the light that shines on an object produces the color that we see. Each color of pigment absorbs its opposite (complementary color) and the rest is reflected back at us as color. This is called “Subtraction.”
- Magenta pigment absorbs green light and reflects red and blue light, which we see as magenta.
- Yellow pigment absorbs blue light and reflects red and green light, which we see as yellow.
- Cyan pigment absorbs red light and reflects green and blue light, which we see as cyan.
The color of the light that is not “subtracted” and reaches our eyes determines what color we see. Light on a black object subtracts all colors and no light is reflected. Light on a white object does not subtract colors and reflects all the colors.
Digital Color Mixing
Color Wheel
A color wheel is an organization of hues around a circle. It is a tool used to help us understand color relationships and is traditional in the field of art and design. Sir Isaac Newton developed the first circular diagram of colors in 1666. Since then, scientists and artists have studied and designed numerous variations of this concept. 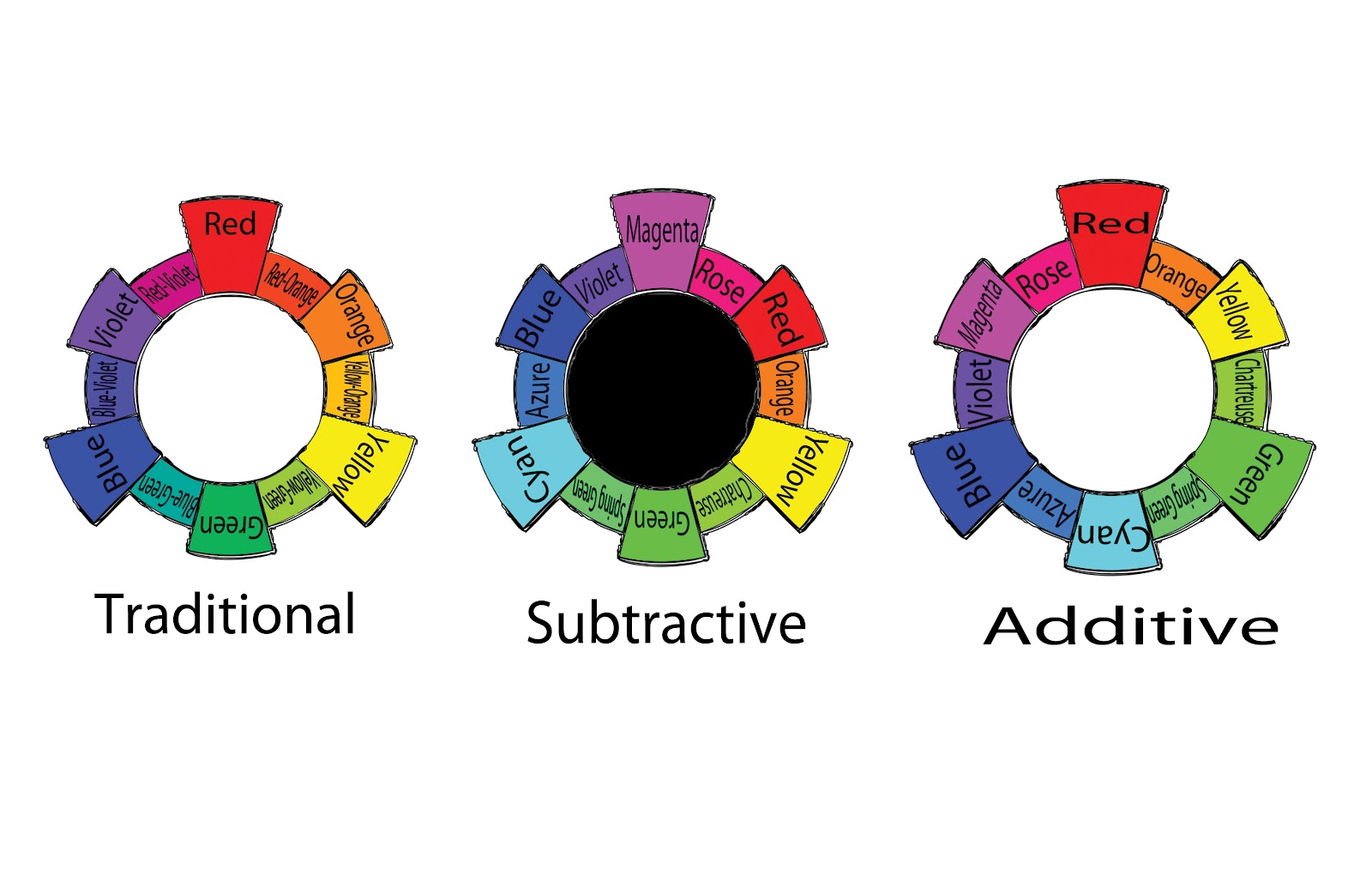
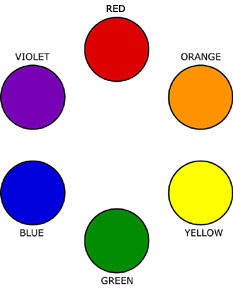
RYB Color Wheel (Traditional)
- Primary Color Triad: Red, Yellow, Blue
- Secondary Color Triad: Orange, Green, Violet
- orange (mix red + yellow)
- green (mix yellow + blue)
- violet (mix blue + red)
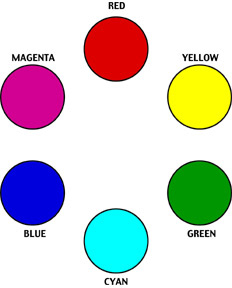
CMY Color Wheel (Contemporary)
- Primary Triad: Cyan, Yellow, Magenta
- Secondary Triad: Red, Green, Blue
- Green (Yellow + Cyan)
- Red (Yellow + Magenta)
- Blue (Cyan + Magenta)
Lab: Color Wheel FreeStudy
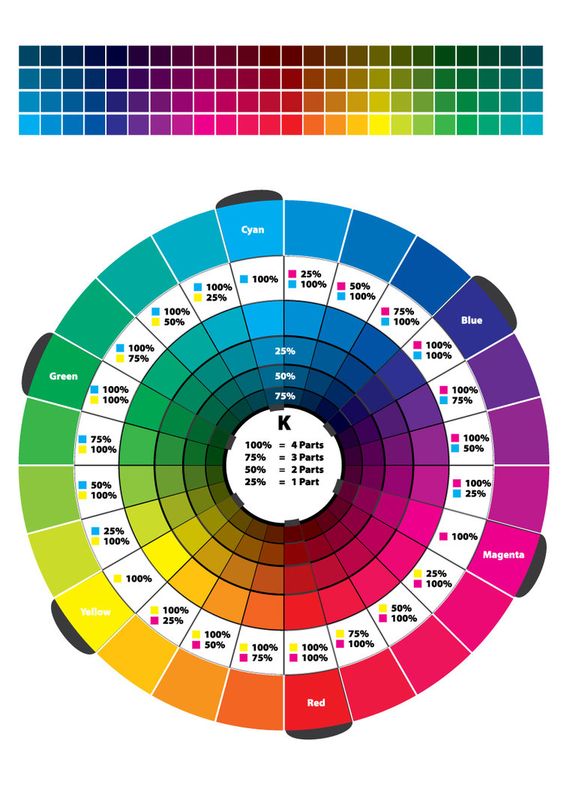
Starter Color Wheel:
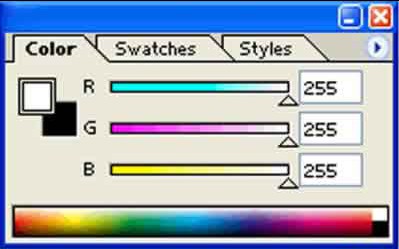
- Using the template file provided, work independently to accurately fill in the color wheel using the Paint Bucket and CMYK Color palette sliders.
- Start with the primary triad from the CYM system (Cyan, Yellow, Magenta)
- Then fill in the RYB system (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet) using the percentages in the color wheel above.
- Save the file as firstintial_lastname_ColorWheel.psd
Unique Color Wheel:
Once you have successfully experimented with the triad relationships (primary and secondary) from both systems, work with your partner to plan out a unique Color Wheel.
- Think about how the colors relate to each other.
- What does each color represent: mood, emotion, object.
- Choose an object, animal or word to represent each color.
- Find hi-quality, free stock images using the sites listed below to visualize your color wheel concept.
- Make sure your final color wheel composition is laid out with a clear connection to the original primaries and secondaries.
- In the Photoshop file, use the Layer Group called YOUR COLOR WHEEL.
- Open your stock images and drag the image layer into your Color Wheel file.
- Create Clipping Masks for each color / image group. Make sure you are doing this in YOUR COLOR WHEEL.
- Each partner will create their own color wheel, based on your shared concept.
Here are some examples of interesting color wheels:
- http://www.colourlovers.com/blog/2007/12/11/unusual-color-wheels-found-in-life-and-art/
- https://www.google.com/search
- Also see in-class examples from past students.
Use the following resources to find free stock photo or royalty-free images:
- Pexels
- Unsplash
- Gratisography
- Morguefile
- Pixabay
- Stockvault
- Picjumbo
- Pikwizard
- Rawpixel
- Reshot
- Creative Commons Search
Export:
- Save your the firstinital_lastname_ColorWheel.psd file.
- Export your STARTER COLOR WHEEL and MY COLOR WHEEL as two separate PNGs by choosing Export > Export As from the File menu.
- Reduce the image size on export to 50%. Use the following settings:
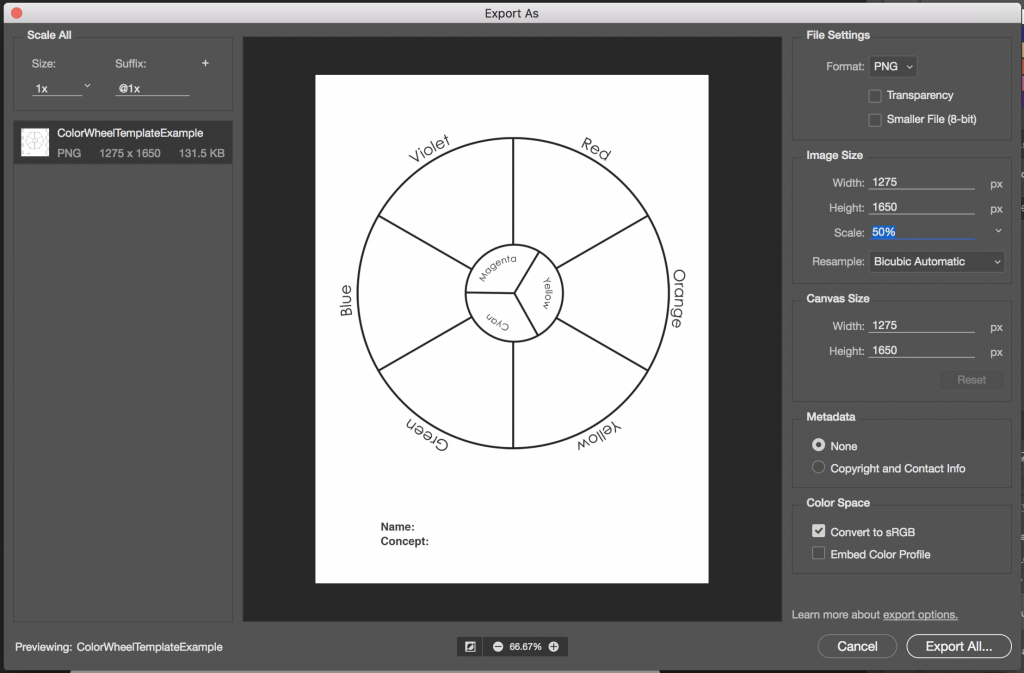
File > Export > Export As
HOMEWORK
DUE: Completed Color Wheel FreeStudy.
- Post an image of 1) your Starter Color Wheel and 2) your unique Color Wheel to the Class Blog (see Phase 1: Discover).
- Don’t forget to comment on at least 1 other student’s posts.
Glossument Reminder: We will have our third critique on November 26th. You should have completed at least 8 visualizations of glossary words and begin thinking about an overall theme or connection between the words.
Supplies Needed for Color Painting!
-
- mini color wheel
- Reeves Gouache 12 Paint Set or Savoir Faire Gouache 10 Paint Set or Utrecht Designer Gouache, Set of 8 – Primaries
- sable-type watercolor brushes
- FLAT: 1/2″ angle, #4
- ROUND: #1, #5
- two water containers
- palette (round 10-well)
- cotton rags (old white t-shirts or scraps)
- pad of Bristol board (9”x12” 2-ply smooth plate finish)